You don't have to put up with discomfort if your job requires you to sit at a desk! By employing appropriate workplace ergonomics, you may be able to prevent health issues linked to desk jobs, such as back and neck pain as well as painful wrists and shoulders. Desk posture, equipment spacing, and chair height all have an impact. By following this approach, you can protect your joints, reduce physical strain on your body, and maintain your comfort level while working.
Chair
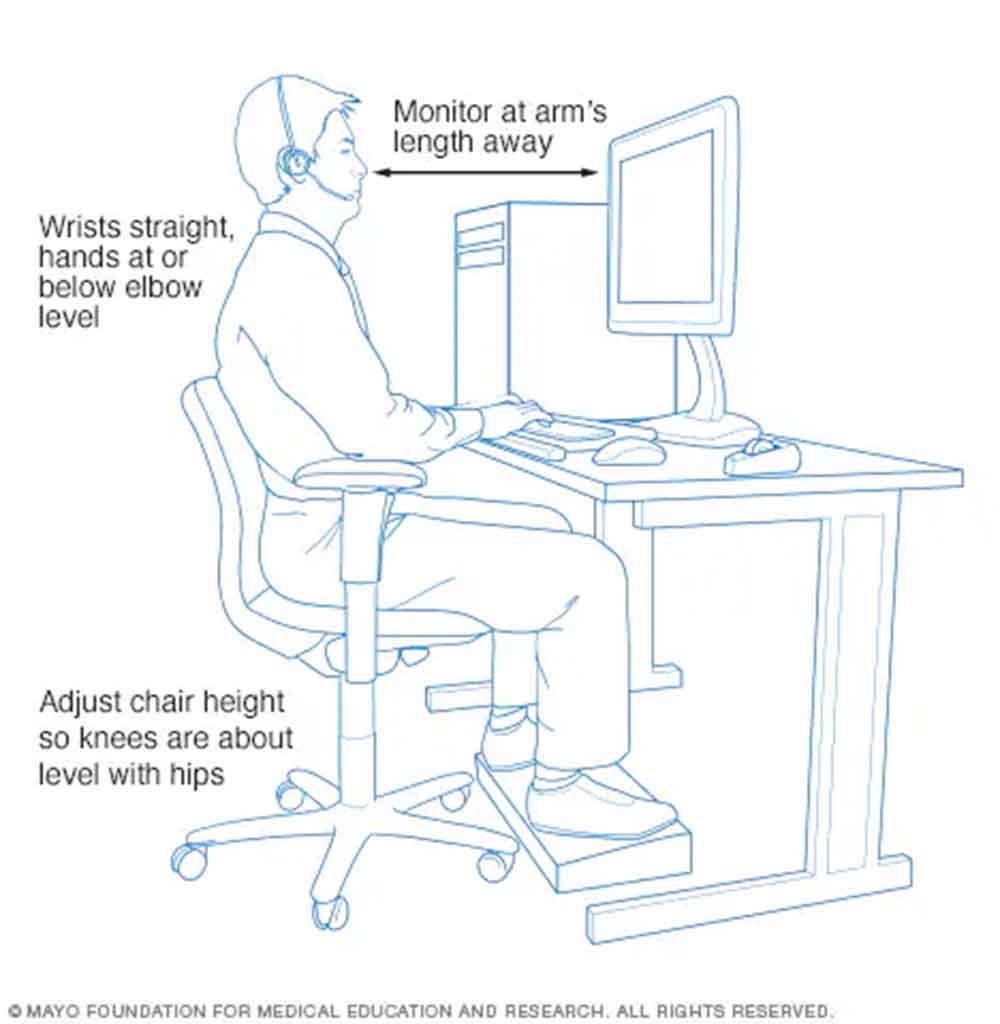
Select a chair that provides back support. Make sure your feet are flat on the floor by adjusting the chair's height. Alternately, position your thighs parallel to the floor by using a footrest. If the chair has armrests, place your arms on them gently, keeping your shoulders relaxed and your elbows close to your body.
Desk
Make sure you have enough space for your legs and feet underneath the desk. Avoid keeping anything under your desk as this can make it difficult to sit comfortably. Place solid boards or blocks beneath the desk legs to raise it if it is too low, and the height cannot otherwise be adjusted. Raise your chair if the desk is too high and cannot be adjusted at all. If you need to support your feet, use a footrest. Try using a little stool or a pile of thick books if you don't have a footrest. Use a wrist rest or cushion the hard edge of your desk if it isn't rounded. This shields your wrists from contact stress, a condition that can arise from prolonged contact with a sharp object.
Mouse And Keyboard
Position your computer keyboard in front of you with your shoulders relaxed and your wrists and forearms aligned. Place your mouse or other computer-connected pointer close to your hand, on the same surface as your keyboard, if you use one. Keep your wrists straight, your upper arms close to your body, and your hands at or slightly below elbow level when typing, using a mouse, or pointing with a computer touchpad. If at all it is feasible, adjust the mouse or pointer's sensitivity so that you can touch it lightly.

Screen Monitor
The distance between you and the monitor should be no more than 20 inches (about 50 centimetres) or 40 inches (about 100 centimetres). The top of the screen needs to be at eye level or just below. For more comfortable viewing, lower the monitor by an extra 1 to 2 inches (about 2 to 5 centimetres) if you wear bifocals.

Phone
Use a headset or put your phone on speaker if you frequently type or write while on the phone, or if you spend a lot of time on the phone. Keep the phone away from your neck and head. Keep in mind that sitting in the same position for extended periods of time is bad for your health, regardless of how well your workstation is configured for ergonomics. Throughout the workday, get up and take as many walks as you can. Try to work while standing if you can. Stretch your hands, fingers, and arms sometimes while seated. You can maintain your health and reduce physical strain by standing up, moving around, and changing positions.
Employ Ergonomic Assistance
It can be difficult to sit at a desk and maintain a neutral posture. It can also be challenging to always be in perfect alignment after years of bad posture patterns. Fortunately, there are top-notch support solutions that promote neutral posture and aid in the development of more ergonomic practices.
The correct office chair is one of the most crucial items for encouraging good posture when using a computer. Many of the adjustable ergonomic office chairs have lumbar support and built-in headrests for improved spine alignment. Office footrests and workstation accessories like keyboard trays and monitor arms are further ergonomic support products.
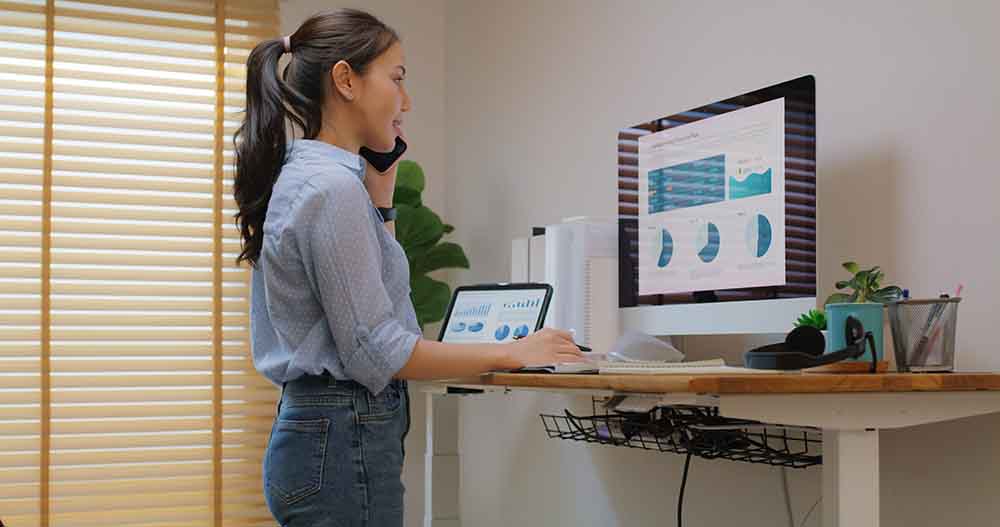

The ‘sit-stand’ desk, an adjustable desk that effortlessly transitions from a sitting to a standing position, is one workplace choice that is becoming more and more popular. According to research, providing employees with a sit-stand desk improved their moods, cut down on sitting time by more than an hour each day, and reduced neck and upper back pain by 54 per cent.
Adopt A Neutral Posture, At Work Or Elsewhere
It goes without saying that using ergonomic items to help spine alignment and maintaining proper posture at work are crucial. Maintaining proper posture at home, when travelling, and elsewhere is equally vital. Preventing chronic, incapacitating illnesses requires maintaining appropriate spine alignment in all facets of life.
Image source: Mayo clinic