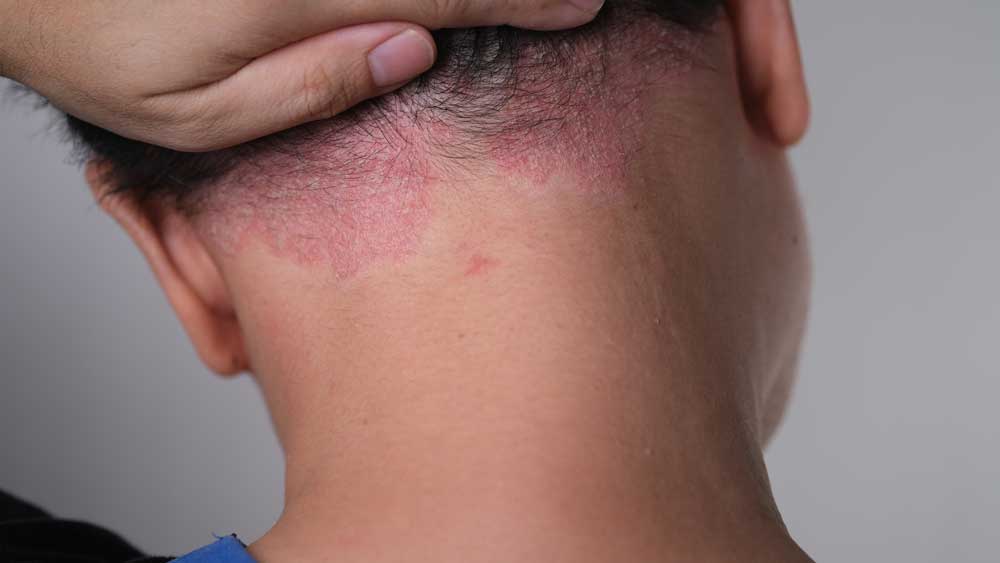
Inflammation is a natural and essential process where the body's immune system responds to any kind of infection or injury. It may show up in various forms such as rashes, redness, swelling, heat and pain. These reactions emerge as the body tries to to neutralise any harmful agents, remove damaged tissues and move forward towards overall healing.
There are two main kinds of inflammation:
1. Acute Inflammation - This occurs when our body responds rapidly to any kind of injury or infection such as cut or burn. Redness, swelling and pain are outward signs of acute inflammation. The moment these reactions appear, it confirms that the body has started its recovery mechanism.
2. Chronic inflammation - This type of inflammation is typically low grade but persistent and can last for years or months.
Chronic inflammation is also connected to various kinds of ailments such as:
• Heart disease
• High blood pressure
• Certain cancers
• Chronic pain
• Type 2 diabetes
• Anxiety
• Depression
• Certain autoimmune conditions

Factors That Cause Inflammation -
• The dietary choices we make
• Smoking and tobacco
• Exercise habits
• Sleep routine
• Alcohol consumption habits
• Persistent viral or bacterial infections
• Allergens and environmental pollutants in the air, water, and food
How To Reduce Inflammation Naturally:
1. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables - Fruits and vegetables are beneficial for strength and recovery. It is advisable to include as many vibrantly coloured varieties as you can, as each has its own unique nutrition and value.
2. Include more fibre in your food - An article by Good Food Is Good Medicine states ’Fibre is essential for our gut health, and therefore our overall health. Most Americans only get about 50 per cent of the recommended daily amount of fibre. Try for 25 grams per day (for women) or 38 grams per day (for men).’
3. Opt for plant-based or lean animal protein sources - Lean animal protein sources include fish, turkey and chicken. If you are a vegetarian, plant-based sources include soy products (tofu, tempeh, edamame, soy milk), beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. It’s also recommended to avoid charring while cooking or barbequing meat products, since it creates compounds that can easily trigger inflammation.
4. Eat high-fibre carbs - Your meal should contain whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat products like bread and pasta, barley, oats, quinoa, buckwheat, and farro. Other equally good options are starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, potatoes, winter squashes, beets, corn, beans, and peas.
5. Be mindful of your fat sources - First and foremost avoid trans fats. They are most likely present in deep-fried food and partially hydrogenated oils. Saturated fats must also be avoided to the large extent - butter, fatty meats, poultry skin, processed meats, cheeses and other high-fat dairy products, coconut oil, palm oil, and cocoa butter. Try opting for unsaturated fats like extra virgin olive oil or avocado oil. Expeller-pressed canola or sunflower oil can be used for higher heat cooking.

6. Reduce the ratio of Omega-6 to Omega-3 - Try making Omega-3 rich foods a norm in your regular diet such with enriched eggs and wild-caught fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, anchovies, sardines, and herring. Plant-based sources include flax seeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts. Ultra-processed foods, including, safflower, corn, grapeseed, and cottonseed oils must be avoided as much as they are rich in Omega-6.
7. Cut down your sugar intake - Avoid processed foods that contain sugar. Those are really harmful, especially in sugary drinks or beverages. Make it a habit to check food labels to understand the portion of sugar in them. Honey and maple syrup are less refined forms of sugar, but still count as added sugars.
8. Limit or avoid alcohol completely - This is one of the quickest ways to ensure reduced inflammation. Alcohol disrupts the gut microbiome and can act as fuel to chronic inflammation.
9. Include tea and spices with anti-inflammatory benefits - Black, white, and green teas are rich in antioxidants and polyphenols that help in reducing inflammatory conditions. Some herbal teas also have anti-inflammatory properties such as rosemary, garlic, oregano, ginger, turmeric, cloves, nutmeg, cinnamon, and cayenne.